What does it mean to model a distribution?
Definition: The manner in which goods move from the manufacturer to the outlet where the consumer purchases them; in some marketplaces, it’s a very complex channel, including distributors, wholesaler, jobbers and brokers.
- Q. What is a distribution model statistics?
- Q. How do you find the probability of a probability model?
- Q. How do you create a probability model?
- Q. What are the different distribution models?
- Q. What are examples of distribution?
- Q. How do you calculate distribution?
- Q. What are the different types of distributions in statistics?
- Q. What are the 3 types of probability?
- Q. What is an example of a probability model?
- Q. What is a uniform probability model give an example?
- Q. What are the 4 types of distribution?
- Q. How is a probability distribution defined in statistics?
- Q. Can a random variable have an equal probability distribution?
- Q. When do you use a binomial probability model?
- Q. How to calculate a binomial distribution in statistics?
Q. What is a distribution model statistics?
A statistical distribution is a parameterized mathematical function that gives the probabilities of different outcomes for a random variable. There are discrete and continuous distributions depending on the random value it models.
Q. How do you find the probability of a probability model?
The ratio for the probability of an event ‘P’ occurring is P (event) = number of favorable outcomes divided by number of possible outcomes.
Q. How do you create a probability model?
How To: Given a probability event where each event is equally likely, construct a probability model.
- Identify every outcome.
- Determine the total number of possible outcomes.
- Compare each outcome to the total number of possible outcomes.
Q. What are the different distribution models?
The three main categories of sales distribution models are:
- Intensive Distribution. Intensive distribution refers to distribution involving a lot of intermediaries.
- Selective Distribution. Selective distribution refers to having just a few intermediaries.
- Exclusive Distribution.
Q. What are examples of distribution?
Distribution is defined as the process of getting goods to consumers. An example of distribution is rice being shipped from Asia to the United States.
Q. How do you calculate distribution?
Calculate the standard deviation of the distribution. Subtract the average of the sample means from each value in the set. Square the result. For example, (6 – 7)^2 = 1 and (8 – 6)^2 = 4.
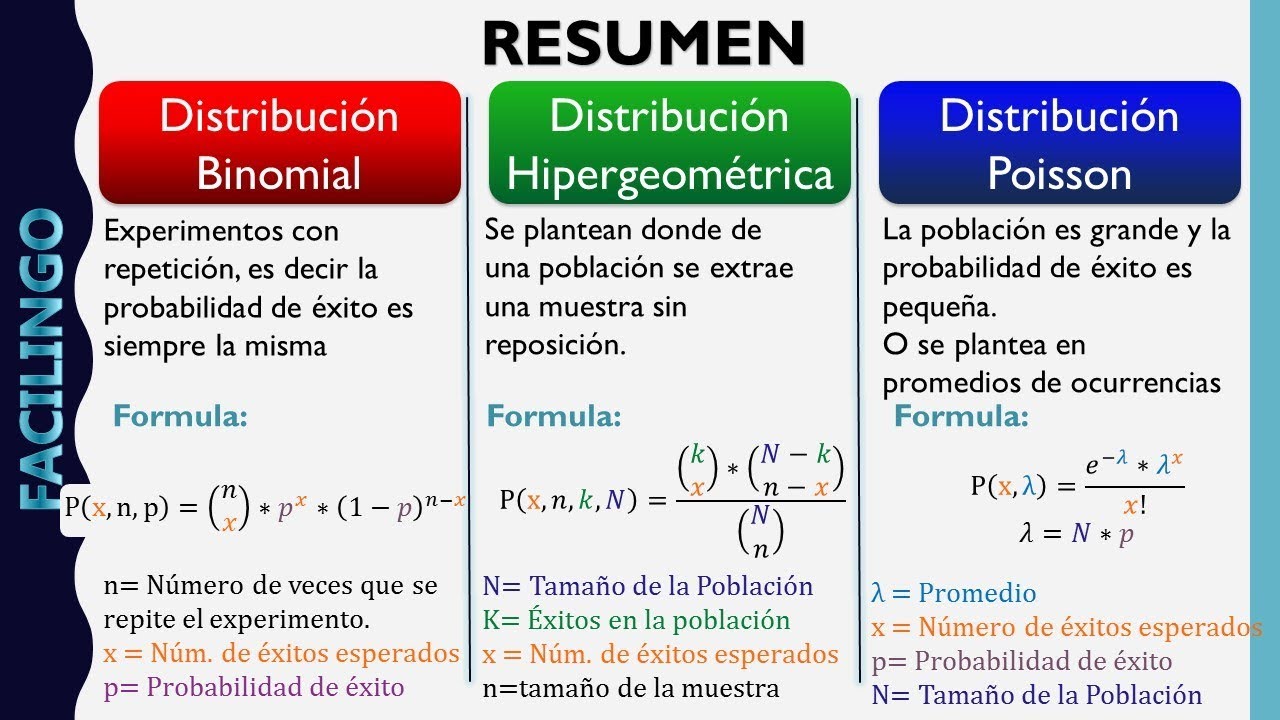
Q. What are the different types of distributions in statistics?
There are many different classifications of probability distributions. Some of them include the normal distribution, chi square distribution, binomial distribution, and Poisson distribution. The different probability distributions serve different purposes and represent different data generation processes.
Q. What are the 3 types of probability?
There are three major types of probabilities:
- Theoretical Probability.
- Experimental Probability.
- Axiomatic Probability.
Q. What is an example of a probability model?
A probability model is a mathematical representation of a random phenomenon. The sample space S for a probability model is the set of all possible outcomes. For example, suppose there are 5 marbles in a bowl. One is red, one is blue, one is yellow, one is green, and one is purple.
Q. What is a uniform probability model give an example?
One well-known example of a uniform probability distribution is found when rolling a standard die. If we assume that the die is fair, then each of the sides numbered one through six has an equal probability of being rolled. There are six possibilities, and so the probability that a two is rolled is 1/6.
Q. What are the 4 types of distribution?
There are four types of distribution channels that exist: direct selling, selling through intermediaries, dual distribution, and reverse logistics channels. Each of these channels consist of institutions whose goal is to manage the transaction and physical exchange of products.
Q. How is a probability distribution defined in statistics?
Probability distribution yields the possible outcomes for any random event. It is also defined based on the underlying sample space as a set of possible outcomes of any random experiment. These settings could be a set of real numbers or a set of vectors or set of any entities. It is a part of probability and statistics.
Q. Can a random variable have an equal probability distribution?
Two random variables with equal probability distribution can yet vary with respect to their relationships with other random variables or whether they are independent of these.
Q. When do you use a binomial probability model?
The binomial distribution model is an important probability model that is used when there are two possible outcomes (hence “binomial”). In a situation in which there were more than two distinct outcomes, a multinomial probability model might be appropriate, but here we focus on the situation in which the outcome is dichotomous.
Q. How to calculate a binomial distribution in statistics?
Formulas Binomial Distribution P (X) = nCxaxbn-x Where a = probability Cumulative Distribution Function Discrete Probability Distribution
Cada distribución de probabilidad tiene sus características propias de aplicación, en el presente vídeo se explica como identificar y cuando aplicar las prin…
No Comments