What is the gravitational pull called?
gravitation
gravity, also called gravitation, in mechanics, the universal force of attraction acting between all matter.
- Q. What does gravitational force pull?
- Q. What is the gravitational pull on Earth today?
- Q. Where is gravity strongest on earth?
- Q. Is gravity a push or a pull?
- Q. Where is the Earth gravitational pull strongest?
- Q. At what height Earth gravity is zero?
- Q. At what height gravity is zero?
- Q. Where is gravity the strongest?
- Q. Why is gravity 32?
- Q. Where is Earth’s gravity weakest?
- Q. What is the definition of gravitational pull?
- Q. Which planet has the most gravitational pull?
- Q. What is the formula for gravitational pull?
- Q. What is the strongest gravity pull?
Q. What does gravitational force pull?
Gravity or gravitational forces are forces of attraction. That pull is gravity at work. Every object in the universe that has mass exerts a gravitational pull, or force, on every other mass. The size of the pull depends on the masses of the objects.
Q. What is the gravitational pull on Earth today?
This means that the gravity of Earth at the equator is 9.789 m/s2, while the force of gravity at the poles is 9.832 m/s2. In other words, you weigh more at the poles than you do at the equator because of this centripetal force, but only slightly more.
Q. Where is gravity strongest on earth?
In the case of the earth, the force of gravity is greatest on its surface and gradually decreases as you move away from its centre (as a square of the distance between the object and the center of the Earth). Of course, the earth is not a uniform sphere so the gravitational field around it is not uniform.
Q. Is gravity a push or a pull?
Gravity is a force, which means that it pulls on things. But the Earth isn’t the only thing which has gravity. In fact, everything in the universe, big or little, has its own pull because of gravity – even you. Isaac Newton was one of the first scientists to figure out the rules of how gravity behaves.
Q. Where is the Earth gravitational pull strongest?
Arctic Ocean
Mount Nevado Huascarán in Peru has the lowest gravitational acceleration, at 9.7639 m/s2, while the highest is at the surface of the Arctic Ocean, at 9.8337 m/s2.
Q. At what height Earth gravity is zero?
Near the surface of the Earth (sea level), gravity decreases with height such that linear extrapolation would give zero gravity at a height of one half of the Earth’s radius – (9.8 m·s−2 per 3,200 km.)
Q. At what height gravity is zero?
Q. Where is gravity the strongest?
In general, the closer the centers of two objects, the greater the force of gravity becomes. Therefore, you would expect gravity in the United States to be stronger wherever you are closest to the center of the Earth.
Q. Why is gravity 32?
Gravity will accelerate any object at a rate of 32 feet per second per second. What it means is that if we fall for one second we’ll reach a speed of 32 feet per second. After two seconds we reach 64 feet per second. The speed rises as the square root of height, but in direct proportion to time.
Q. Where is Earth’s gravity weakest?
equator
In addition, gravity is weaker at the equator due to centrifugal forces produced by the planet’s rotation. It’s also weaker at higher altitudes, further from Earth’s centre, such as at the summit of Mount Everest.
Q. What is the definition of gravitational pull?
Gravitational pull is the hidden force that causes massive objects to pull other objects towards them. For instance, when a person jumps up in the air, it is the earth’s gravitational pull that causes him to return to the ground. All massive objects have gravity, and the bigger they are,…
Q. Which planet has the most gravitational pull?
the most massive one : Jupiter. The largest and most massive planet has the greatest gravitational force: Jupiter. the most massive one : Jupiter.
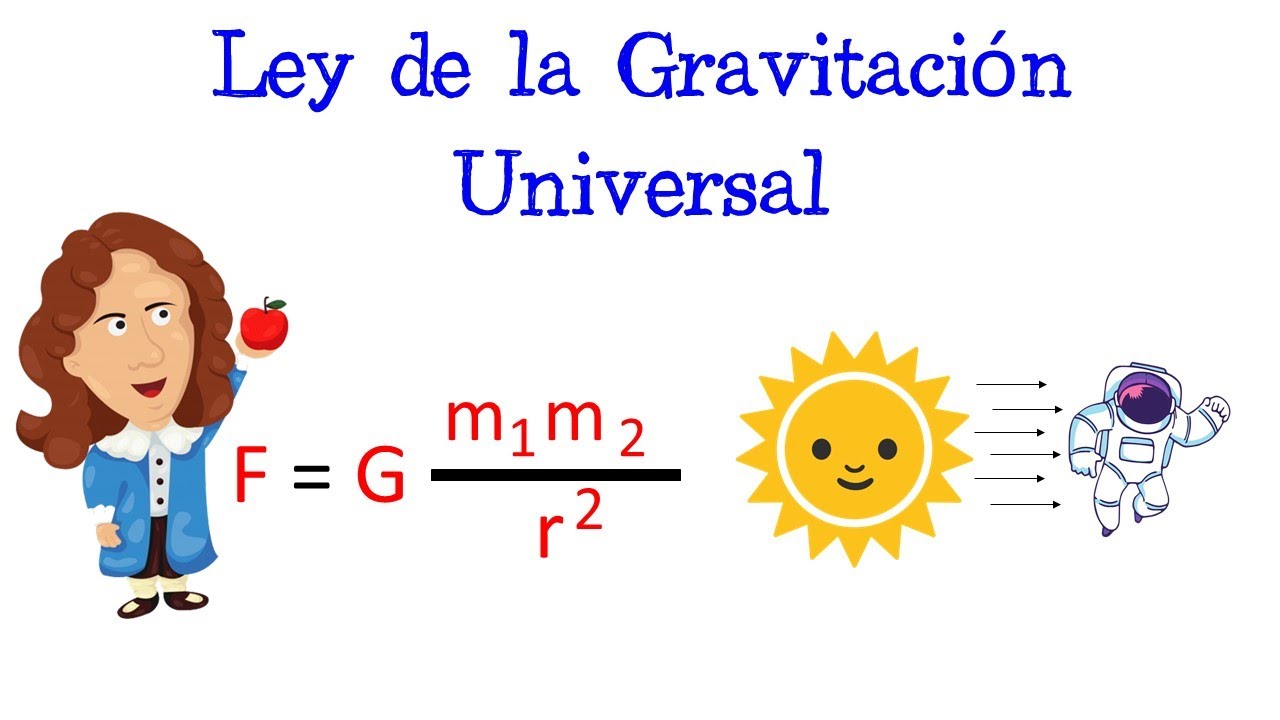
Q. What is the formula for gravitational pull?
Use the following formula to calculate the gravitational force between any two objects: F = G * M * m / R^2. F stands for gravitational force. It is measured in newtons and is always positive.
Q. What is the strongest gravity pull?
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, has the strongest gravitational pull because it’s the biggest and most massive.
ACC te enseña y explica paso a paso la Ley de la Gravitación Universal en 1 minuto de forma rápida y sencilla#Ley #Newton #Gravitación #Universal #LeyGravita…
No Comments